Sum of subsets
Sum of subsets
Solution 01:
A recursive solution for subset sum proble.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
map<int , int>M;
bool isSubsetsum(int set[], int n, int sum)
{
// cout << "Enter-------"<<endl;
if(sum == 0)return true;
if(n == 0 && sum != 0)return false;
///If last element is greater than sum, then ignore it
if(set[n-1] > sum)return isSubsetsum(set, n-1, sum);
/// else, inluding last element || excluding last element
return (isSubsetsum(set, n-1, sum) || isSubsetsum(set, n-1, sum - set[n-1]) );
}
int main()
{
/* #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif*/
//int set[] = {3,34, 4, 12, 5, 2};
int set[12345];
int sum = 9;
//int n = sizeof(set)/sizeof(set[0]);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> set[i];
}
if(isSubsetsum(set, n, sum)){
cout << "Found a subset with given sum";
}
else {
cout << "No subset with given sum";
}
return 0;
}
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
map<int , int>M;
bool isSubsetsum(int set[], int n, int sum)
{
// cout << "Enter-------"<<endl;
if(sum == 0)return true;
if(n == 0 && sum != 0)return false;
///If last element is greater than sum, then ignore it
if(set[n-1] > sum)return isSubsetsum(set, n-1, sum);
/// else, inluding last element || excluding last element
return (isSubsetsum(set, n-1, sum) || isSubsetsum(set, n-1, sum - set[n-1]) );
}
int main()
{
/* #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif*/
//int set[] = {3,34, 4, 12, 5, 2};
int set[12345];
int sum = 9;
//int n = sizeof(set)/sizeof(set[0]);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> set[i];
}
if(isSubsetsum(set, n, sum)){
cout << "Found a subset with given sum";
}
else {
cout << "No subset with given sum";
}
return 0;
}
Solution 02: DP
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
map<int , int>M;
bool isSubsetsum(int set[], int n, int sum)
{
// cout << "Enter-------"<<endl;
bool subset[n+1][sum+1];
if(sum == 0)return true;
/// If sum is 0, then answer is true
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++)subset[i][0] = true;
/// If sum is not 0 and set is empty, then answer is false
for(int i = 1; i <= sum; i++)subset[0][i] = false;
///Fill the subset table in bottom up manner
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= sum; j++){
if(j < set[i-1])
subset[i][j] = subset[i-1][j] || subset[i-1][j-set[i-1]];
}
}
/// this code to print table
/**for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j <= sum; j++)
{
printf("%4d",subset[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}**/
return subset[n][sum];
}
int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
//int set[] = {3,34, 4, 12, 5, 2};
int set[12345];
int sum = 9;
//int n = sizeof(set)/sizeof(set[0]);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> set[i];
}
if(isSubsetsum(set, n, sum)){
cout << "Found a subset with given sum";
}
else {
cout << "No subset with given sum";
}
return 0;
}
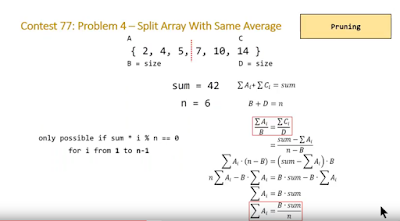
805. Split Array With Same Average
805. Split Array With Same Average
class Solution {
return false;
**/
Topic: pruning + DP.
Copmplexity: O(n^3).
Soltion:
Code:
class Solution {
public:
bool is_possible(int m, int sum, int n)
{
bool possible = false;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
if(sum*i % n == 0)possible = true;
return possible;
}
bool splitArraySameAverage (const vector<int>& A)
{
int n = A.size();
int m = n/2;
int sum = accumulate(A.begin(), A.end(), 0);
if(!is_possible(m,sum,n)) return false;///pruning
vector<unordered_set<int> > ans(m+1);
ans[0].insert(0);
for(int num : A)
for(int i = m; i >= 1; i--)
for(int t : ans[i-1])
ans[i].insert(t+num);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
if(sum*i %n == 0 && ans[i].find(sum*i/n) != ans[i].end())return true;
}
return false;
/**
| sums[0].insert (0); |
| for (int num : A) |
| for (int i = m; i >= 1; --i) |
| transform (sums[i - 1].begin (), sums[i - 1].end (), |
| inserter (sums[i], sums[i].end ()), |
| [num](int t) { return t + num; }); |
| for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) |
| if (sum * i % n == 0 && sums[i].count (sum * i / n)) return true; |
**/
| vector<unordered_set<int>> sums (m + 1); |
}
};
Bus Routes
815. Bus Routes
complexity : O(n)
Topic: BFS
Eplanation
class Solution {
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
public:
int numBusesToDestination(vector<vector<int> >& routes, int S, int T)
{
unordered_map<int, unordered_set<int> > stop_routes;
for(int i = 0; i < routes.size(); i++){
for(int j : routes[i])stop_routes[j].insert(i);
}
queue<pair<int, int> > to_visit;
to_visit.push({S,0});
unordered_set<int>stop_visited = { S };
while(!to_visit.empty()){
int stop = to_visit.front().first;
int bus_n = to_visit.front().second;
if(stop == T)return bus_n;
to_visit.pop();
for(const auto& route : stop_routes[stop]){
for(const auto& next_stop : routes[route]){
auto it = stop_visited.insert(next_stop);
if(it.second)to_visit.push({next_stop, bus_n+1});
}
routes[route].clear();
}
}
return -1;
}
};
Consecutive Numbers Sum
829. Consecutive Numbers Sum
class Solution {
O( sqrt(N) )
Solution:
Code:
class Solution {
public:
int consecutiveNumbersSum(int N)
{
int ans = 0;
for(int n = 2; n*(n+1)/2 <= N; ++n){
if( (N - n*(n+1)/2) %n == 0)ans++;
}
return ans+1;
}
};
Shortest Bridge
934. Shortest Bridge
using island = set<pair<int, int> >;
};
Problem Type: Recursion; Flood Fill.
Code:
using island = set<pair<int, int> >;
using vi = vector<int>;
using vvi = vector<vi>;
class Solution{
public:
int n;
vi dx = {0, 0, 1, -1};
vi dy = {1, -1, 0, 0};
bool is_valid(int x, int y){
return (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n);
}
void flood_fill(island& A, const vvi& g, int x, int y){
A.insert({x,y});
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = x + dy[i];
if(is_valid(nx, ny) && g[nx][ny] && !A.count({nx, ny})){
flood_fill(A, g, nx, ny);
}
}
}
template<class T>
int dist(T a, T b){
return abs(a.first - b.first) + abs(a.second - b.second) - 1;
}
int shortestBridge(vvi& g){
n = g.size();
island A, B;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(g[i][j] == 0)continue;
if(A.empty())
flood_fill(A, g, i,j);
else if(B.empty() && !A.count({i,j}))
flood_fill(B, g, i, j);
}
}
int ans = 2*n;
for(auto i: A){
for(auto j: B){
ans = min(ans, dist(i,j));
}
}
return ans;
}
};Groups of Special-Equivalent Strings
893. Groups of Special-Equivalent Strings
public:
int numSpecialEquivGroups(vector<string>& A) {
unordered_set<string> s;
for(const auto& w: A){
string odd, even;
for(int i = 0; i < w.size(); i++){
if(i%2) even += w[i];
else odd += w[i];
}
sort(even.begin(), even.end());
sort(odd.begin(), odd.end());
s.insert(even+odd);
}
return s.size();
}
};
CODE:
class Solution {public:
int numSpecialEquivGroups(vector<string>& A) {
unordered_set<string> s;
for(const auto& w: A){
string odd, even;
for(int i = 0; i < w.size(); i++){
if(i%2) even += w[i];
else odd += w[i];
}
sort(even.begin(), even.end());
sort(odd.begin(), odd.end());
s.insert(even+odd);
}
return s.size();
}
};
Minimum Falling Path Sum
931. Minimum Falling Path Sum
1 2 3 4 ------------- 1 2 3 4
4 -1 3 -2 ------------- 5 0 5 1
-2 5 -3 2 ------------- -2 4 -3 3
7 -6 9 8 ------------- 5 -9 6 5
minimun element = -9.
time complexity = O(n^2)
Code:
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using vi = vector<int>;
using vvi = vector<vi>:
int minFallingpathsum(vector<vector>>& a){
int n =a.size();
vvi dp(n,vi(n));
dp[0] = a[0];
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
dp[i][j] = a[i][j] + dp[i-1][j];
if(j > 0)
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], a[i][j]+dp[i-1][j-1]);
if(j < n- 1)dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], dp[i-1][j+1]);
}
}
return *min_element(dp[n-1].begin(), dp[n-1].end());
}
1 2 3 4 ------------- 1 2 3 4
4 -1 3 -2 ------------- 5 0 5 1
-2 5 -3 2 ------------- -2 4 -3 3
7 -6 9 8 ------------- 5 -9 6 5
minimun element = -9.
time complexity = O(n^2)
Code:
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using vi = vector<int>;
using vvi = vector<vi>:
int minFallingpathsum(vector<vector>>& a){
int n =a.size();
vvi dp(n,vi(n));
dp[0] = a[0];
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
dp[i][j] = a[i][j] + dp[i-1][j];
if(j > 0)
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], a[i][j]+dp[i-1][j-1]);
if(j < n- 1)dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], dp[i-1][j+1]);
}
}
return *min_element(dp[n-1].begin(), dp[n-1].end());
}
Tiling Problem/Defective chessboard problem
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int team[500][500],cnt=1,m;
void room(int x1, int y1, int X, int Y, int nx, int ny)
{
if(cnt > m)return;
if(abs(x1 - nx) <= 1 && abs(y1 - ny)<= 1){
for(int i = x1; i <= nx; i++){
for(int k = y1; k <= ny; k++){
if(team[i][k] == 0)team[i][k] = cnt;
}
}
cnt++;
return;
}
int mid_x = (x1+nx)/2;
int mid_y = (y1+ny)/2;
//cnt++;
if(X > mid_x){///lower
if(Y > mid_y){
///lower_right
//cnt++;
team[mid_x][mid_y] = cnt;
team[mid_x][mid_y+1] = cnt;
team[mid_x+1][mid_y] = cnt;
cnt++;
room(x1, y1, mid_x, mid_y, mid_x, mid_y);
room(x1, mid_y+1, mid_x, mid_y+1, mid_x, ny);
room(mid_x+1,y1, mid_x+1, mid_y, nx, mid_y);
room(mid_x+1, mid_y+1, X, Y, nx, ny);
}
else{
///lower_left
// cnt++;
team[mid_x][mid_y] = cnt;
team[mid_x][mid_y+1] = cnt;
team[mid_x+1][mid_y+1] = cnt;
cnt++;
room(x1, y1, mid_x, mid_y, mid_x, mid_y);
room(x1, mid_y+1, mid_x, mid_y+1, mid_x, ny);
room(mid_x+1,y1, X, Y, nx, mid_y);
room(mid_x+1, mid_y+1, mid_x+1, mid_y+1, nx, ny);
}
}
else{///upper
if(Y > mid_y){
///upper_right
//cnt++;
team[mid_x][mid_y] = cnt;
team[mid_x+1][mid_y] = cnt;
team[mid_x+1][mid_y+1] = cnt;
cnt++;
room(x1, y1, mid_x, mid_y, mid_x, mid_y);
room(x1, mid_y+1, X, Y, mid_x, ny);
room(mid_x+1,y1, mid_x+1, mid_y, nx, mid_y);
room(mid_x+1, mid_y+1, mid_x+1, mid_y+1, nx, ny);
}
else{
///upper_left
//cnt++;
team[mid_x+1][mid_y] = cnt;
team[mid_x][mid_y+1] = cnt;
team[mid_x+1][mid_y+1] = cnt;
cnt++;
room(x1, y1, X, Y, mid_x, mid_y);
room(x1, mid_y+1, mid_x, mid_y, mid_x, ny);
room(mid_x+1,y1, mid_x+1, mid_y, nx, mid_y);
room(mid_x+1, mid_y+1, mid_x+1, mid_y+1, nx, ny);
}
}
return;
}
int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
int sz;
cin >> m;
/// here m is the total team number.
int ck = m*3 + 1;
for(int i = 0; i <32; i++){
int valid = 1 << i;
int ckk= valid*valid;
if(ckk >= ck){
sz = valid;
break;
}
}
cout << sz << endl;
int X = rand()%sz;
int Y = rand()%sz;
//cout << X << " "<<Y<<endl;
team[X][Y] = -1;
room(1,1,X,Y,sz,sz);
// cout << "ENter----------"<<endl;
for(int i = 1; i <= sz; i++){
for(int k = 1; k <= sz; k++){
if(i==X&&k==Y)cout << setw(5)<<"X";
else
cout << setw(5)<<team[i][k];
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
using namespace std;
int team[500][500],cnt=1,m;
void room(int x1, int y1, int X, int Y, int nx, int ny)
{
if(cnt > m)return;
if(abs(x1 - nx) <= 1 && abs(y1 - ny)<= 1){
for(int i = x1; i <= nx; i++){
for(int k = y1; k <= ny; k++){
if(team[i][k] == 0)team[i][k] = cnt;
}
}
cnt++;
return;
}
int mid_x = (x1+nx)/2;
int mid_y = (y1+ny)/2;
//cnt++;
if(X > mid_x){///lower
if(Y > mid_y){
///lower_right
//cnt++;
team[mid_x][mid_y] = cnt;
team[mid_x][mid_y+1] = cnt;
team[mid_x+1][mid_y] = cnt;
cnt++;
room(x1, y1, mid_x, mid_y, mid_x, mid_y);
room(x1, mid_y+1, mid_x, mid_y+1, mid_x, ny);
room(mid_x+1,y1, mid_x+1, mid_y, nx, mid_y);
room(mid_x+1, mid_y+1, X, Y, nx, ny);
}
else{
///lower_left
// cnt++;
team[mid_x][mid_y] = cnt;
team[mid_x][mid_y+1] = cnt;
team[mid_x+1][mid_y+1] = cnt;
cnt++;
room(x1, y1, mid_x, mid_y, mid_x, mid_y);
room(x1, mid_y+1, mid_x, mid_y+1, mid_x, ny);
room(mid_x+1,y1, X, Y, nx, mid_y);
room(mid_x+1, mid_y+1, mid_x+1, mid_y+1, nx, ny);
}
}
else{///upper
if(Y > mid_y){
///upper_right
//cnt++;
team[mid_x][mid_y] = cnt;
team[mid_x+1][mid_y] = cnt;
team[mid_x+1][mid_y+1] = cnt;
cnt++;
room(x1, y1, mid_x, mid_y, mid_x, mid_y);
room(x1, mid_y+1, X, Y, mid_x, ny);
room(mid_x+1,y1, mid_x+1, mid_y, nx, mid_y);
room(mid_x+1, mid_y+1, mid_x+1, mid_y+1, nx, ny);
}
else{
///upper_left
//cnt++;
team[mid_x+1][mid_y] = cnt;
team[mid_x][mid_y+1] = cnt;
team[mid_x+1][mid_y+1] = cnt;
cnt++;
room(x1, y1, X, Y, mid_x, mid_y);
room(x1, mid_y+1, mid_x, mid_y, mid_x, ny);
room(mid_x+1,y1, mid_x+1, mid_y, nx, mid_y);
room(mid_x+1, mid_y+1, mid_x+1, mid_y+1, nx, ny);
}
}
return;
}
int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
int sz;
cin >> m;
/// here m is the total team number.
int ck = m*3 + 1;
for(int i = 0; i <32; i++){
int valid = 1 << i;
int ckk= valid*valid;
if(ckk >= ck){
sz = valid;
break;
}
}
cout << sz << endl;
int X = rand()%sz;
int Y = rand()%sz;
//cout << X << " "<<Y<<endl;
team[X][Y] = -1;
room(1,1,X,Y,sz,sz);
// cout << "ENter----------"<<endl;
for(int i = 1; i <= sz; i++){
for(int k = 1; k <= sz; k++){
if(i==X&&k==Y)cout << setw(5)<<"X";
else
cout << setw(5)<<team[i][k];
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Large Number Factorial
>> Large Number Factorial:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define FastIO ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
#define INF 10000000
#define MAX 500
int multiply(int x, int res[], int res_size);
void factorial(int n)
{
int res[MAX];
res[0] = 1;
int res_size = 1;
for(int x = 2; x <= n; x++){
res_size = multiply(x, res, res_size);
}
//cout << "factorial of Given NUmber is \n";
for(int i = res_size - 1; i >= 0; i--)
cout << res[i];
cout << endl;
}
int multiply(int x, int res[], int res_size)
{
int carry = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < res_size; i++){
int prod = res[i]*x + carry;
res[i] = prod % 10;
carry = prod/10;
}
while(carry){
res[res_size] = carry%10;
carry = carry/10;
res_size++;
}
return res_size;
}
int main()
{
FastIO;
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
int n;
cin >> n;
while(n--){
int n;
cin >> n;
factorial(n);
}
return 0;
}